Largest Rectangle in Histogram
Given n non-negative integers representing the histogram’s bar height where the width of each bar is 1, find the area of largest rectangle in the histogram.
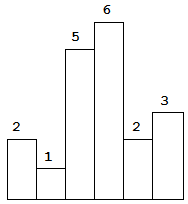
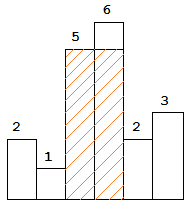
Above is a histogram where width of each bar is 1, given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3].
The largest rectangle is shown in the shaded area, which has area = 10 unit. For example, Given height = [2,1,5,6,2,3], return 10.
题目链接在这里
O(n2)
这道题目最为朴素的解法时间复杂度为O(n2),简单的枚举所有的点对作为区间的起点和终点,并计算所围成的最大矩形面积并找到最大值即可。 但是显然,这样做太低效了。
O(nlogn)
更近一步,我们可以得到一个基于分治思想时间复杂度为O(nlogn)解法: 对于任何一个区间,我们首先找到这个区间中的最低点,则这个区间中最大的矩形面积为如下三种情况的最大值:
- 最低点左边区间中的最大矩形面积
- 最低点右边区间中的最大矩形面积
- 最低点作为矩形的高所围成的矩形面积
这样我们就得到了一个分治解法,如下:
class Solution
{
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &height)
{
return maxArea(height, 0, height.size());
}
private:
int maxArea(vector<int> &height, int l, int r)
{
if (l >= r) {
return 0;
}
int min = height[l];
int index = l;
if (l >= r) {
return 0;
}
for (int i = l; i < r; ++i) {
if (height[i] < min) {
min = height[i];
index = i;
}
}
int left = maxArea(height, l, index);
int right = maxArea(height, index + 1, r);
int ans = (r - l) * min;
if (left > ans) {
ans = left;
}
if (right > ans) {
ans = right;
}
return ans;
}
};
O(nlogn)的解法对这道题目来说还不够好,更悲剧的上面的O(nlogn)解法存在最差情况:当输入序列为递增序列时,这个解法会退化为O(n2),这是我们不能够接受的。
O(n)
O(n)算法相比上面两种方法来说更加的巧妙,其基本思路是:对输入序列中的每一项,都得到以该项作为最低点所能围成的最大矩形面积,并得到其中的最大值作为解。 这个思路的正确性是显然的,为了有效的实现这个思路,在过程中维护了一个存放序列索引的栈,对输入序列依次遍历:
- 当输入项大于栈顶索引对应的输入项时,将输入项索引入栈
- 当输入项小于栈顶索引对应的输入项时,不断出栈栈顶索引直到输入项大于栈顶索引对应的输入项。同时,对每个出栈的栈顶索引:以该索引对应的输入项为最低点的矩形的左边界为栈内前一个元素–新的栈顶(因为栈内元素的递增的),而右边界就是当前正在遍历的输入项,因此可以在O(1)的时间内计算出这个矩形的面积。
- 当遍历结束后如果栈不为空,则对栈依次出栈并执行步骤2
看下代码就明白了:
class Solution
{
public:
int largestRectangleArea(vector<int> &height)
{
return getMaxArea(height, height.size());
}
private:
// The main function to find the maximum rectangular area under given
// histogram with n bars
// http://www.geeksforgeeks.org/largest-rectangle-under-histogram/
int getMaxArea(vector<int> &hist, int n)
{
// Create an empty stack. The stack holds indexes of hist[] array
// The bars stored in stack are always in increasing order of their
// heights.
stack<int> s;
int max_area = 0; // Initalize max area
int tp; // To store top of stack
int area_with_top; // To store area with top bar as the smallest bar
// Run through all bars of given histogram
int i = 0;
while (i < n)
{
// If this bar is higher than the bar on top stack, push it to stack
if (s.empty() || hist[s.top()] <= hist[i])
s.push(i++);
// If this bar is lower than top of stack, then calculate area of rectangle
// with stack top as the smallest (or minimum height) bar. 'i' is
// 'right index' for the top and element before top in stack is 'left index'
else
{
tp = s.top(); // store the top index
s.pop(); // pop the top
// Calculate the area with hist[tp] stack as smallest bar
area_with_top = hist[tp] * (s.empty() ? i : i - s.top() - 1);
// update max area, if needed
if (max_area < area_with_top)
max_area = area_with_top;
}
}
// Now pop the remaining bars from stack and calculate area with every
// popped bar as the smallest bar
while (s.empty() == false)
{
tp = s.top();
s.pop();
area_with_top = hist[tp] * (s.empty() ? i : i - s.top() - 1);
if (max_area < area_with_top)
max_area = area_with_top;
}
return max_area;
}
};
Comments